Manufacturing Process
FOCUS
ON EVERY DETAIL
OF THE PROCESS
Full cycle Production
Our company is defined as vertical production. High technology combined with constant innovation enables us to carry out every phase of the manufacturing process in-house. This complete cycle starts with the initial design of the prototype and goes through all stages of machining until the final product is ready for delivery
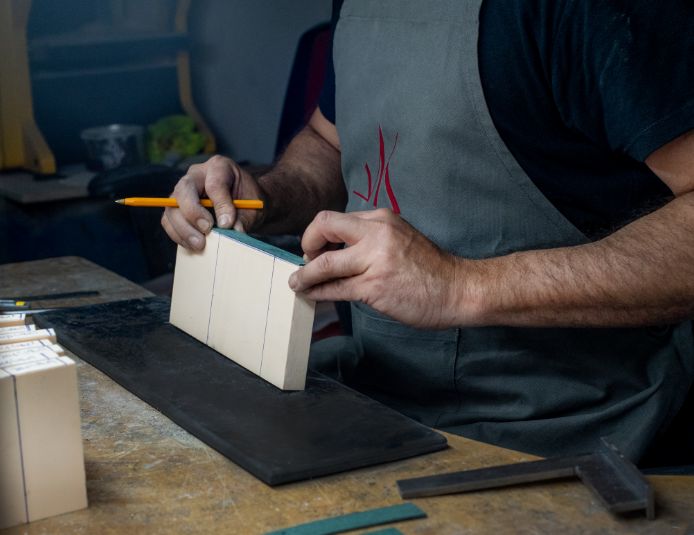

1. Design – Modeling
The experience of our craftsmen in hand modelling, combined with the use of state-of-the-art machinery and cutting equipment, enables us to create prototypes for a wide variety of models, from the most simple to the most complex. In this way, we give shape and form to both our own ideas and those of our customers.
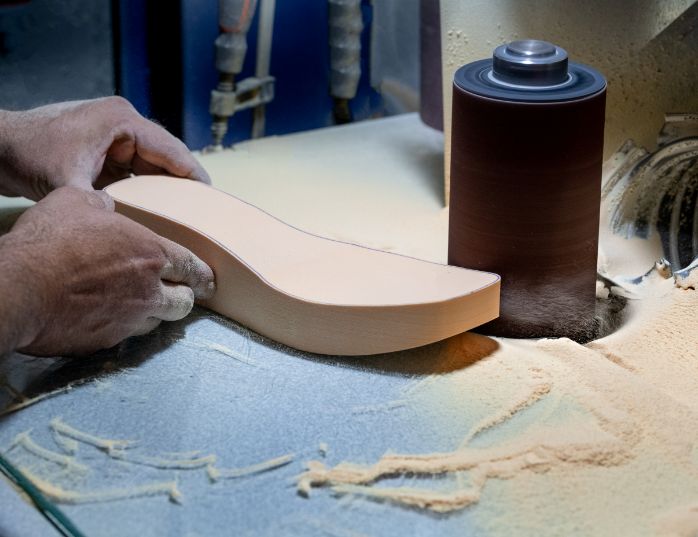
2. Molds Making
The design process is continued in the internal production of moulds, which guarantees quality and confidentiality for our customers. Over the years, we have invested in machinery and equipment for mould casting and production. Opting for state-of-the-art software and technology, we guarantee maximum efficiency and productivity to our customers.
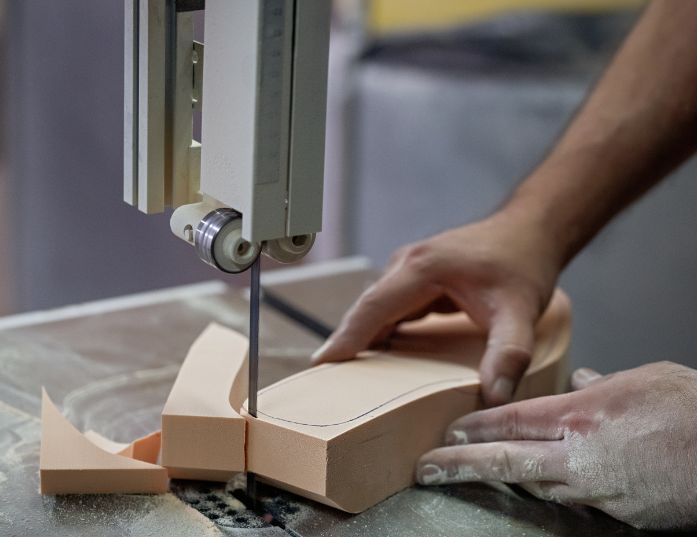
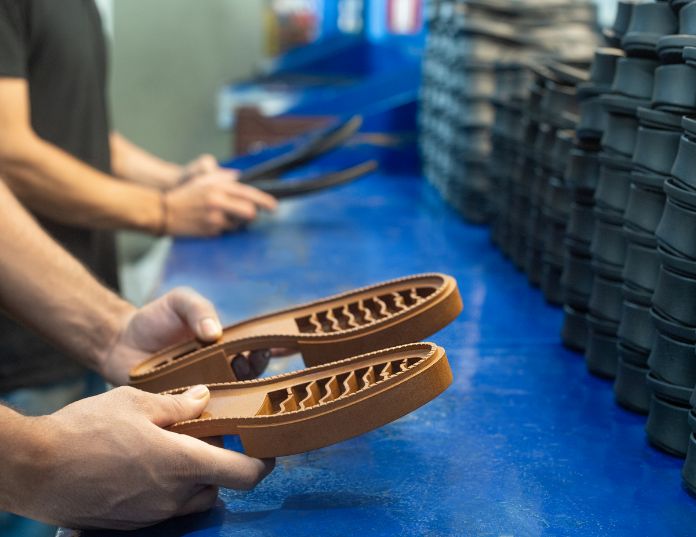


3. Quality Control
After the production stage is completed, the final product is checked through a standardised, rigorous process to ensure that it meets all required specifications. The quality of our products is guaranteed by the use of fine, environmentally friendly materials, while our constant research into innovations offers us even greater efficiency and improvement.
4. Production – Packaging
With the passage of time and the evolution of the production process, we have assured the possibility to provide our customers with the combination of quality and quantity. Due to the excellent organisation and modernised production machines, we can produce any number of pairs per day – from the smallest order to several thousands – taking care of their excellent packaging and shipping From the very receipt of the order, we maintain constant communication with our customers, informing them about the soonest possible time and method of delivery.

You have more question?
ANSWERS
I need a sole in a specific color
We can manufacture our products in specific colours.
Contact us for more details.
What is TPU?
A thermoplastic is a plastic material, usually a polymer, that becomes flexible or malleable above a certain temperature and solidifies on cooling. Most thermoplastics have a high relative molecular mass. The polymer chains are linked by intermolecular forces, which weaken rapidly with increasing temperature, producing a viscous liquid. Therefore, thermoplastics can be reshaped by heating and are commonly used to produce parts for injection molding. Thermoplastics differ from thermosetting plastics, which form irreversible chemical bonds during the curing process.Thermosets do not melt, but decompose and do not reshape on cooling. Thermoplastic material stress-strain plot. Above its glass transition temperature, Tg and below its melting point, Tm, the physical properties of a thermoplastic change drastically without an associated phase transformation. Within this temperature range, most thermoplastics are elastic due to alternating rigid crystalline and elastic amorphous regions, which approach random helices. Some thermoplastics that are not fully crystallized below the glass transition temperature Tg retain some or all of their amorphous characteristics. Amorphous and semi-amorphous plastics are used when high optical clarity is necessary because light is strongly scattered by crystallites larger than their wavelength. Amorphous and semi-amorphous plastics are less resistant to chemical attack and environmental stress cracking because they lack crystalline structure. Brittleness can be reduced by adding plasticizers, which increase the mobility of the amorphous chain segments for an effective lower Tg. Modification of the polymer through copolymerization or through the addition of nonreactive side chains to the monomers prior to polymerization can also lower the Tg. Before the implementation of these techniques, plastic parts of vehicles often broke when exposed to cold temperatures. Recently, thermoplastic elastomers have become available.
Do I have to choose from specific designs?
Our products are available in a variety of sizes, designs, types, and colours.
We can also create products tailored to the individual customer’s wish and exclusive use.
What is PVC?
Polyvinyl chloride (polyvinyl chloride or poly(vinyl chloride)), or abbreviated PVC, is the third most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer, after polyethylene and polypropylene. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible. The rigid form of PVC is used in the construction of pipes, doors and windows. Also used for bottles, other non-food packaging, and cards (such as bank or membership cards). It can be made softer and more pliable by adding plasticizers, the most widely used being phthalates. In this form, it is also used in hydraulics, electrical cable insulation, imitation leather, signage, inflatable products, and many applications where it replaces tires.
Pure polyvinyl chloride is a white, friable solid. It is insoluble in alcohol, but slightly soluble in tetrahydrofuran.